
It is worth mentioning that different researchers may apply different techniques while dealing with number tables. The researcher needs to continue with the same process to select 5 samples, the aim that was set at the beginning. In this case, the first sample selected is 15838, as the first three digits are 158, a number the researcher has assigned to a member of the population. As the researcher has not assigned any member of the population with that number, the search continues! He/she needs to continue to go down the table to find a number between 001 to 200. Let us assume that the number selected is 81666. The researcher then closes his/her eyes and touches a number on the table above to select the first sample. As three digits are being used, the first three digits will be considered from 001 to 200. The target is to select 5 samples.Īs the researcher has a target population of 200, he/she should use the first three digits as 200 is a three-digit number. Let us first assume that a researcher has a total population of 200 students, each of whom has been assigned with a number from 1 to 200. A table like the following one could be useful. They can then put all these numbers in a box/bowl/jar to choose samples randomly, perhaps even closing their eyes!Īnother method is the use of a random number table. From this, they can select random samples by using any of the following methods they like:Īs the name suggests, lottery method of sampling allows researchers to provide each member of the target population with a unique number. They usually make a list of all the target population and afterwards mark each member with a specific number. lottery method of sampling and random number table. It is not unusual for researchers to select their first random number at random by closing their eyes! They often use two methods of simple random sampling i.e.
RANDOM SAMPLING TECHNIQUES HOW TO
How to do simple random sampling (Methods of simple random sampling) In line with the above example, processing the details of 25,000 students will be surely costly. Simple random sampling can sometimes be very costly as well. If the university has 25,000 students, then it can be easily imagined how difficult and time-consuming this process can be. This will require the researchers to put the names of the students into a box or something to choose samples randomly. Let us imagine that the university agrees to provide the researchers with all the names of the students. For instance, if a researcher would like to do a research on the teaching quality and student satisfaction at a university, he/she may find it extremely difficult to have access to the details of the students as the university may be unwilling to share because of the internal policies and data protection concerns. Having access to the details of the potential research respondents can be challenging. There are a number of disadvantages of using simple random sampling in quantitative market research as follows: It also works as the basis for other probability sampling methods (Encyclopaedia Britannica, 2020).Īnother advantage is that this method is easy to assess sampling error. It is usually easy to use, particularly when the size of the target population is small. Simple random sampling is less complicated compared to many other sampling methods. As the researchers select potential respondents very randomly, each individual has the same chance of being selected.
RANDOM SAMPLING TECHNIQUES FREE
Unlike other sampling methods, simple random sampling is bias and prejudice free however, the condition is that it must be applied appropriately. There are a number of advantages of using simple random sampling in quantitative market research as follows: It is also sometimes simply called random sampling. It is where every member of the population has an equal probability (chance) of being selected. Simple random sampling involves selecting the sample at random from the sampling frame using either random number or a computer (Saunders et al., 2007).

Like all other research tools, simple random sampling has its advantages and disadvantages. Sampling is a key part of any research, and many quantitative researchers use simple random sampling for the purpose of data collection.

This article aims to identify and explain some of the advantages and disadvantages of simple random sampling.
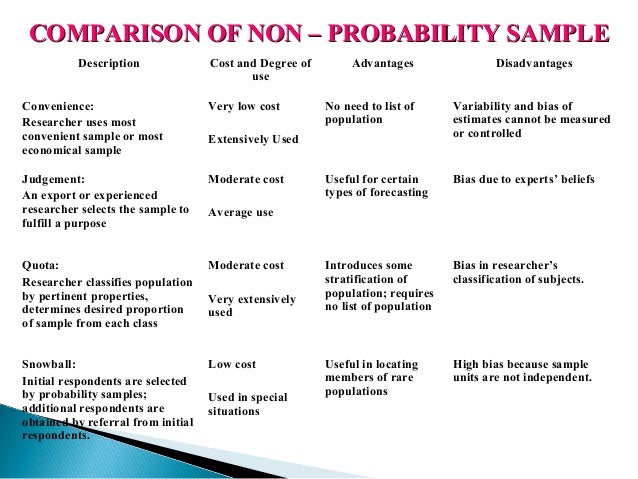
Advantages and disadvantages of simple random sampling


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
